[Day 1] What is Artificial Intelligence?
Dive into the world of Artificial Intelligence—discover how AI, Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Deep Learning, Generative AI, and Large Language Models are transforming industries, unlocking creativity, and reshaping our future in real-time.
![[Day 1] What is Artificial Intelligence?](/content/images/size/w2000/2025/03/_--visual-selection--2-.svg)
Imagine a world where machines understand us and create with us. From automating mundane tasks to sparking unparalleled human creativity, Artificial Intelligence (AI) transforms how we live and work. It's the silent genius behind detecting diseases with unmatched precision, rewriting vague emails into professional masterpieces, and even curing illnesses that haven’t been named yet. Today, ChatGPT is like 'Einstein in your pocket', he just knows everything.
It crafts movies that adapt as you watch, generates art that defies human imagination, and designs personalized experiences that make every product and service feel tailor-made just for you. It predicts natural disasters before they strike and turns
AI is more than algorithms; it's a creative partner. It crafts movies that adapt as you watch, generates art that defies human imagination, and designs personalized experiences that make every product and service feel tailor-made just for you. It predicts natural disasters before they strike and turns unimaginable ideas into tangible realities.
This isn’t some distant dream—it’s happening now, reshaping the world around us at the speed of thought. Let’s embark on this journey to understand AI from the ground up and discover how it’s not just a technological revolution, but a bridge to a future we’re creating together.
Let’s re-arrange the concepts: AI, Machine Learning (ML), Neural Networks (NNs), Deep Learning (DL), Generative AI (GenAI), and Large Language Models (LLMs).
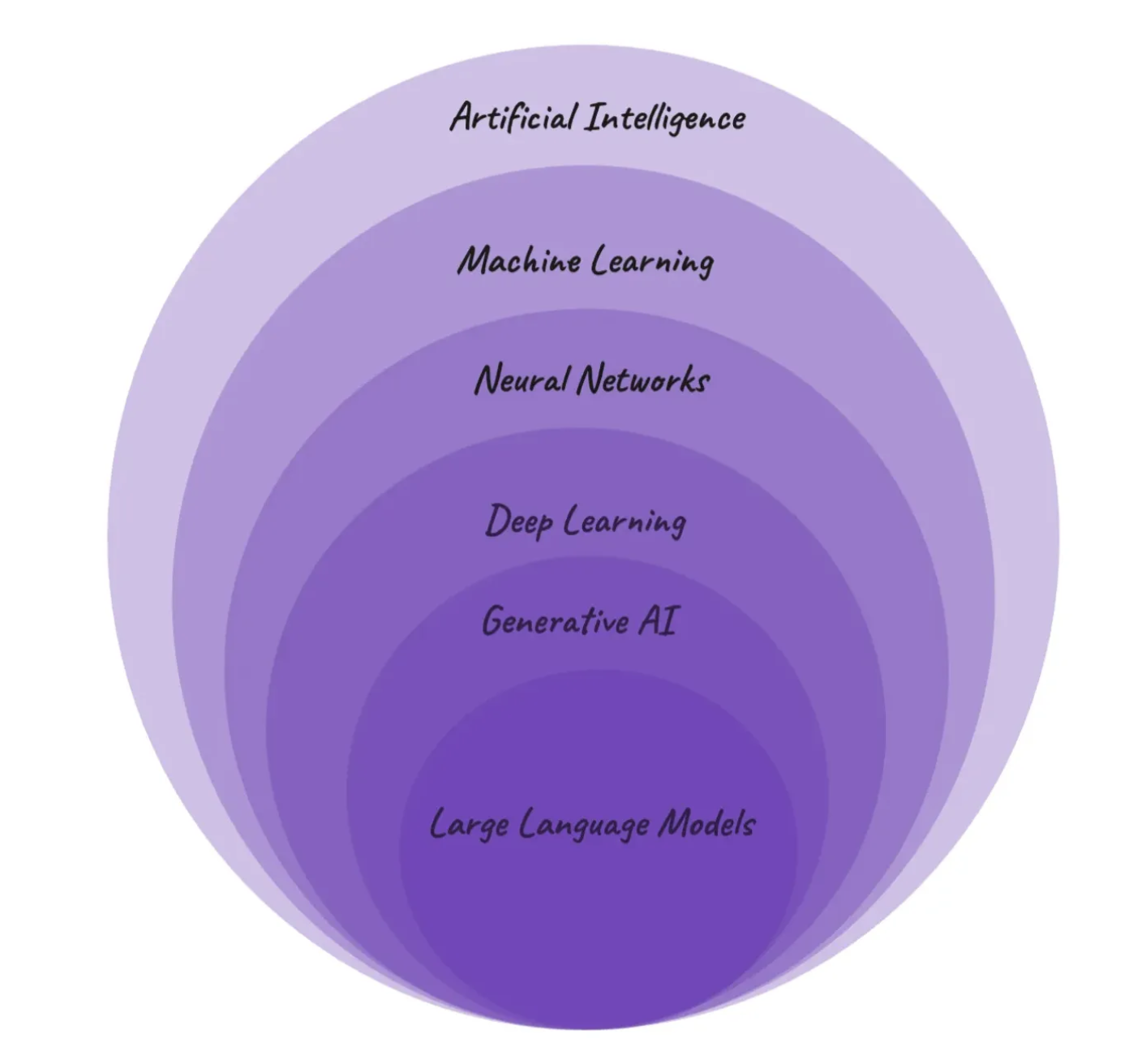
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
“Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence in machines, enabling them to perform tasks such as reasoning, learning, problem-solving, and adapting based on data.”
AI refers to developing computer systems capable of performing tasks traditionally requiring human intelligence, such as problem-solving, decision-making, and understanding natural language.
AI systems range from Narrow AI (focused on specific tasks, like virtual assistants or recommendation engines) to the yet-to-be-realized General AI, which could perform any cognitive function a human can. AI underpins advancements across industries, powering everything from smart devices to autonomous vehicles. By mimicking human intelligence, AI continues to push boundaries in creativity, productivity, and problem-solving.
2. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is a subset of AI where machines learn patterns from data and make predictions without explicit programming. It uses algorithms to process vast datasets and improve its performance over time.
Types:
- Supervised Learning: Models trained on labeled data to classify or predict outcomes, such as spam detection or fraud analysis.
- Unsupervised Learning: Discovering hidden patterns in unlabeled data, such as customer segmentation.
- Reinforcement Learning: Teaching systems to make decisions through trial and error, often used in robotics and gaming, ML powers everyday applications like Netflix’s recommendation engine and predictive text, making our interactions with technology more seamless and personalized.
Will discuss in detail about these in later days.
3. Neural Networks (NNs)
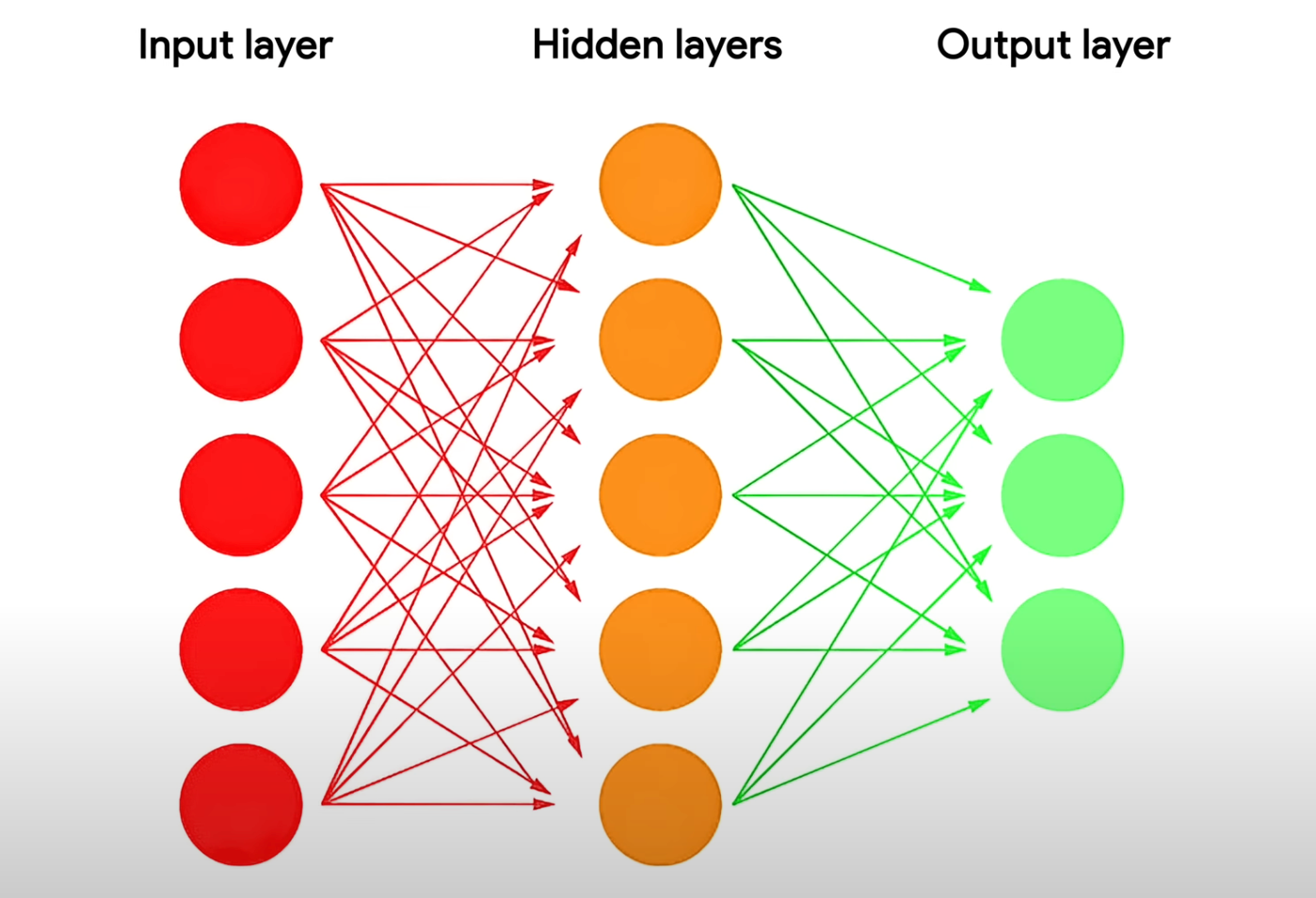
Neural Networks are computational systems inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain. They consist of interconnected nodes (neurons) organized into layers:
- Input Layer: Processes raw data, such as an image or text.
- Hidden Layers: Extract and refine features using weighted connections.
- Output Layer: Produces the final prediction or result.
NNs excel at recognizing patterns in data and are foundational to advanced AI. They power applications like facial recognition, voice assistants, and fraud detection. By simulating human-like learning, neural networks have unlocked breakthroughs in fields like computer vision, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
Probably the best video on the Internet to understand what NN is:
4. Deep Learning (DL)
Deep Learning, a subset of Machine Learning, leverages large datasets and multi-layered neural networks to solve complex problems. These systems automatically extract features from raw data, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
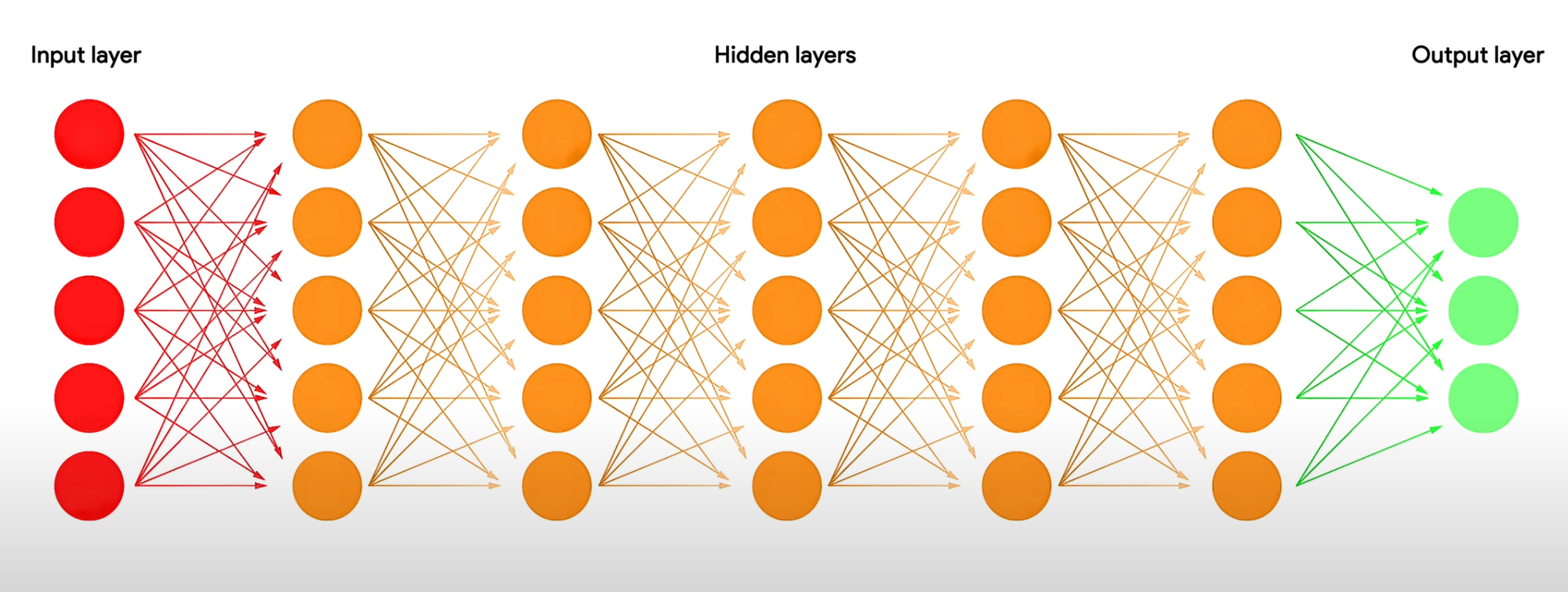
Deep Learning achieves state-of-the-art results by scaling with data and computational power. It has transformed industries by solving problems once considered too complex for machines, such as interpreting emotions in text or creating lifelike digital avatars.
Machine learning has two main types of models: discriminative and generative.
- Discriminative Models:
These focus on identifying or classifying data. For example, they can determine whether an email is spam or not spam or whether a picture contains a cat or a dog. - Generative Models:
These focus on creating or generating new data. For example, they can generate realistic-looking photos of people or write human-like text responses like ChatGPT.
5. Generative AI (GenAI)
Generative AI focuses on creating new, original content based on patterns it learns from data. Unlike discriminative models that classify or predict, GenAI generates entirely new outputs such as:
- Text: Writing articles, stories, or even poetry.
- Images: Producing lifelike visuals or artistic renditions.
- Music: Composing soundtracks or unique melodies.
GenAI’s creative potential is reshaping industries, from automating marketing content to revolutionizing game design. It empowers users to innovate and imagine beyond traditional limitations, turning ideas into reality with unprecedented speed and ease.
6. Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large Language Models (LLMs) are advanced computer programs designed to understand and generate human language. They are trained on vast amounts of text data, such as books, articles, and websites, to learn patterns, grammar, and the meaning of words. This enables them to perform a wide range of language-related tasks, such as answering questions, writing essays, translating languages, and even engaging in human-like conversations.
Essentially, they function as highly intelligent tools powered by artificial intelligence, capable of processing and creating text in a way that feels natural and meaningful. Examples of LLMs include models like ChatGPT, Google’s Bard, and OpenAI’s GPT series.
Powered by transformer architectures, LLMs deliver unmatched scalability and performance, transforming how businesses and individuals interact with technology. They bridge the gap between machine intelligence and human communication.
Why 2017 Changed Everything
Before 2017, AI models processed information sequentially, meaning they analyzed text one word at a time in order. This approach made it difficult for them to understand and handle context efficiently, especially in long sentences or complex texts.
This changed with Google’s introduction of the transformer architecture, revolutionizing AI and natural language processing (NLP).
AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, Bard, and Claude are all based on transformer architectures. It uses attention mechanisms to process and understand language efficiently, enabling these models to excel at tasks like generating, summarizing, and understanding text.
Interesting Fact: The attention mechanism in transformers mimics human focus, prioritizing the most relevant parts of information to make decisions.
Nutshell
- AI is the overarching concept of intelligent systems.
- ML focuses on learning patterns from data.
- Deep Learning takes it further with multi-layered networks for solving advanced problems.
- Generative AI creates entirely new content.
- LLMs, the pinnacle of GenAI, redefine human-computer interaction.
"Imagine a world where AI doesn't just automate but creates, inspires, and transforms industries. That future isn’t tomorrow—it’s today.”
💬 Join the DecodeAI WhatsApp Channel for regular AI updates → Click here